Artist Rendering of NISAR

NISAR will measure Earth’s changing ecosystems, dynamic surfaces, and ice masses providing information about biomass, natural hazards, sea level rise, and groundwater, and will support a host of other applications.
NISAR will observe Earth’s land and ice-covered surfaces globally with 12-day regularity on ascending and descending passes, sampling Earth on average every 6 days for a baseline 3-year mission.
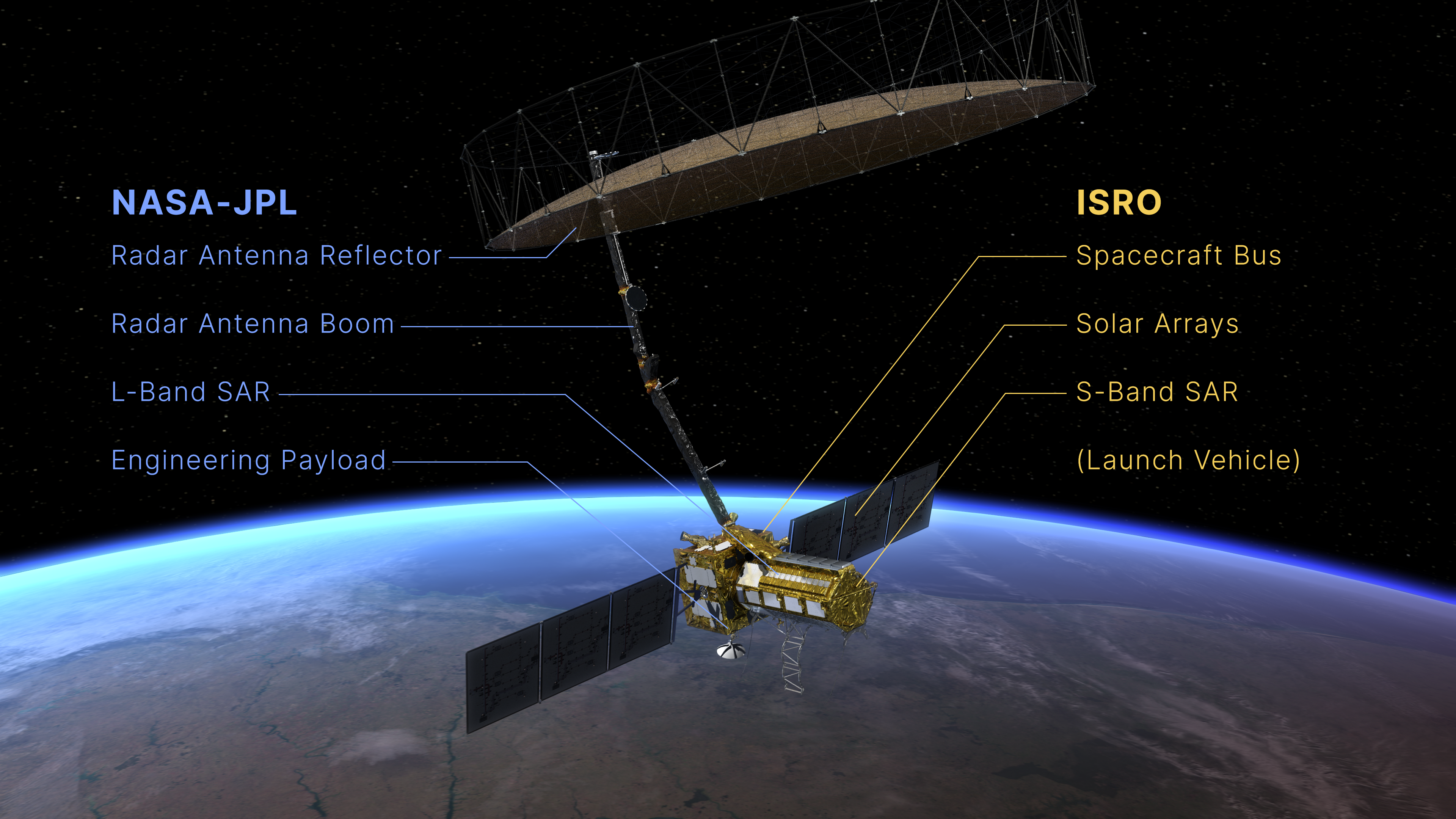
Figure A is an annotated version, listing key hardware contributions to NISAR from NASA-JPL and ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation). NASA-JPL is providing the mission’s radar antenna reflector, radar antenna boom, L-band synthetic aperture radar, and an engineering payload featuring power, data, communications, and GPS systems. ISRO is providing the spacecraft bus, solar arrays, and S-band synthetic aperture radar, along with the mission’s launch vehicle.